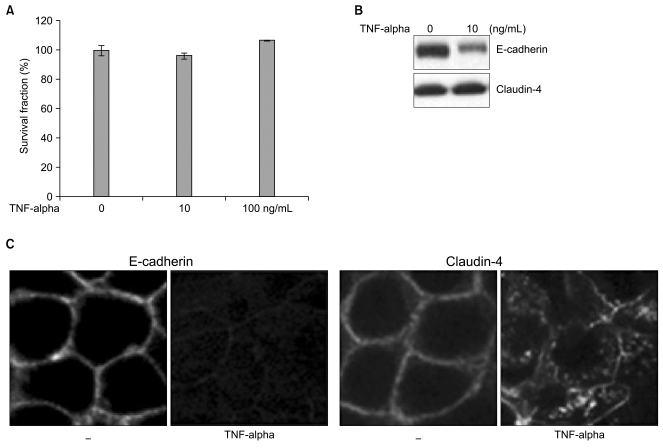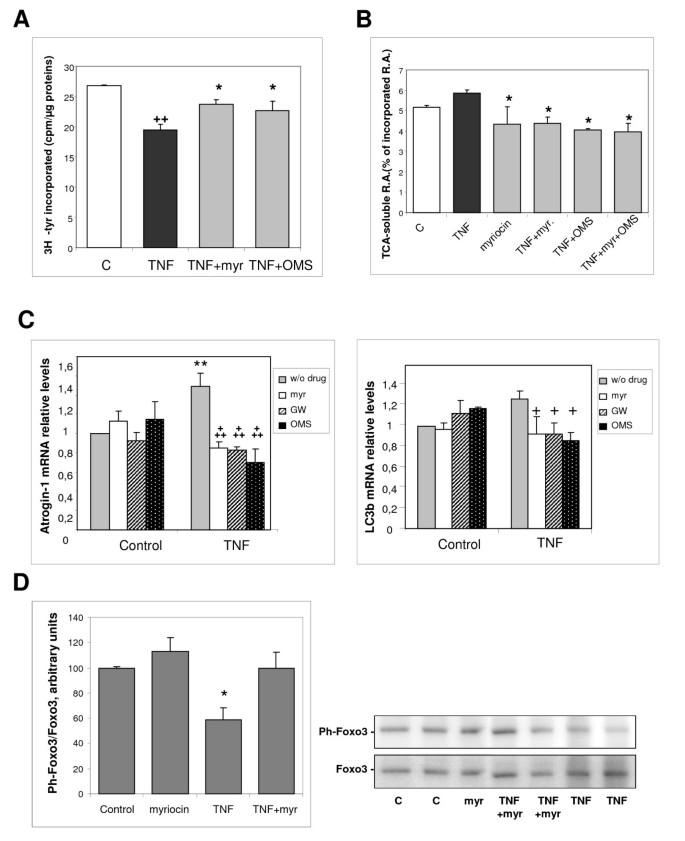
TNF-α- and tumor-induced skeletal muscle atrophy involves sphingolipid metabolism | Skeletal Muscle | Full Text
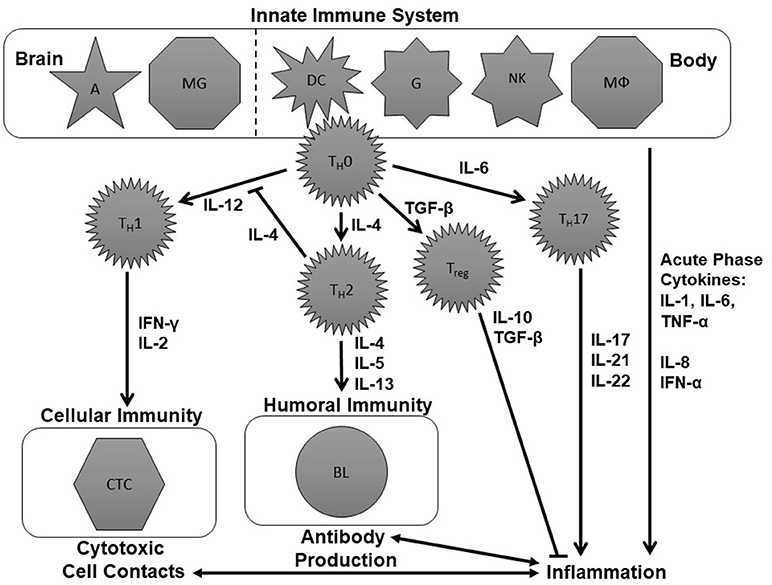
Frontiers | Cytokine Research in Depression: Principles, Challenges, and Open Questions | Psychiatry

Involvement of Sphingosine Kinase in TNF-α-stimulated Tetrahydrobiopterin Biosynthesis in C6 Glioma Cells∗ - Journal of Biological Chemistry

Current therapeutic strategies for respiratory diseases using mesenchymal stem cells - Wang - 2021 - MedComm - Wiley Online Library

SphK1 and intracellular S1P are necessary for NF-κB activation by TNF-α... | Download Scientific Diagram
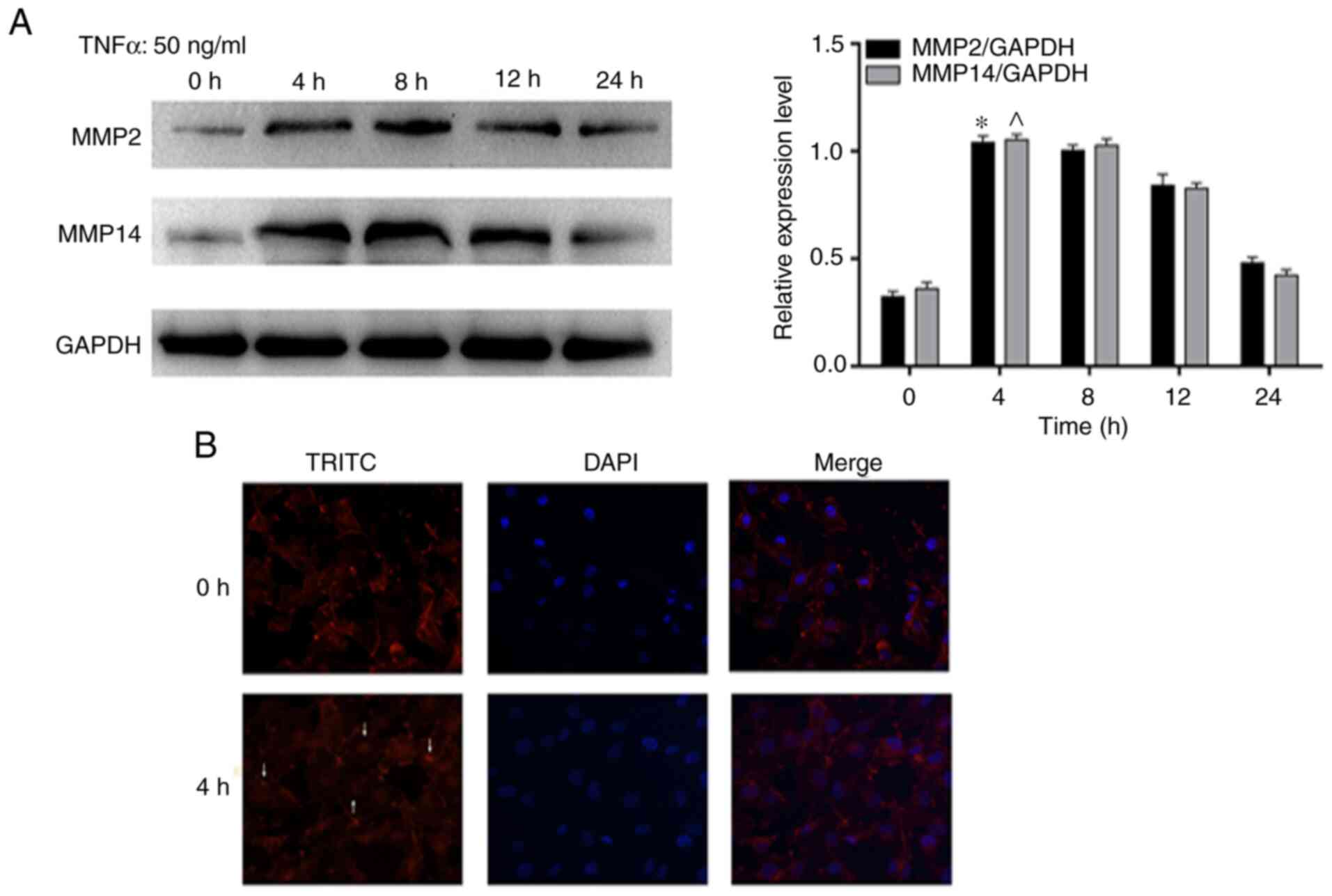
Phosphorylated form of pyruvate dehydrogenase α1 mediates tumor necrosis factor α‑induced glioma cell migration
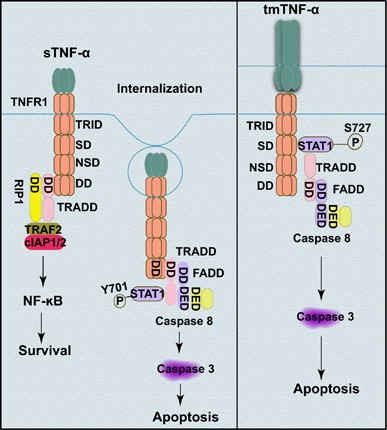
STAT1 mediates transmembrane TNF-alpha-induced formation of death-inducing signaling complex and apoptotic signaling via TNFR1 | Cell Death & Differentiation

TNF-α-Induced Sphingosine 1-Phosphate Inhibits Apoptosis Through a Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase/Akt Pathway in Human Hepatocytes | The Journal of Immunology

The Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha and Interleukin 6 Auto-paracrine Signaling Loop Controls Mycobacterium avium Infection via Induction of IRF1/IRG1 in Human Primary Macrophages | mBio
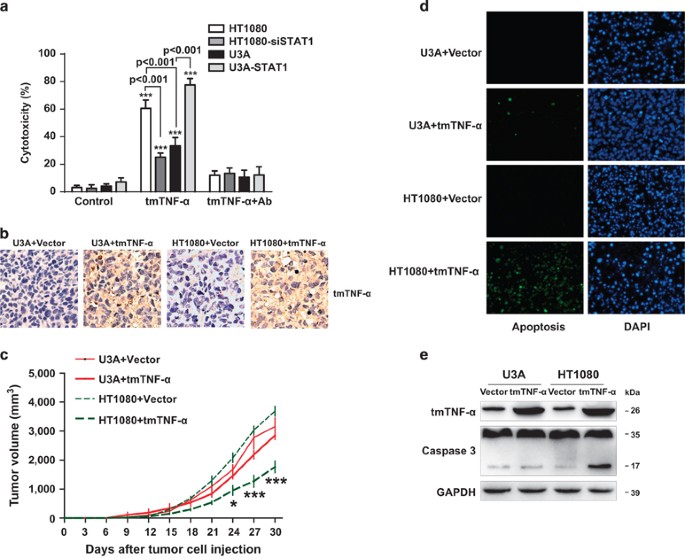
STAT1 mediates transmembrane TNF-alpha-induced formation of death-inducing signaling complex and apoptotic signaling via TNFR1 | Cell Death & Differentiation

Activation of Sphingosine Kinase by Tumor Necrosis Factor-α Inhibits Apoptosis in Human Endothelial Cells* - Journal of Biological Chemistry

Endothelial Cell Inflammatory Responses to Tumor Necrosis Factor α: CERAMIDE-DEPENDENT AND -INDEPENDENT MITOGEN-ACTIVATED PROTEIN KINASE CASCADES - ScienceDirect

Schematic Representation of Signaling Pathways Involved in TNF-α or... | Download Scientific Diagram

Tumor Necrosis Factor-α-stimulated Cell Proliferation Is Mediated through Sphingosine Kinase-dependent Akt Activation and Cyclin D Expression* - Journal of Biological Chemistry

Tumor Necrosis Factor-α and Fas Activate Complementary Fas-associated Death Domain-dependent Pathways That Enhance Apoptosis Induced by γ-Irradiation* - Journal of Biological Chemistry

Tumor Necrosis Factor-α Enhances Microvascular Tone and Reduces Blood Flow in the Cochlea via Enhanced Sphingosine-1-Phosphate Signaling | Stroke

Successful Antidepressant Therapy Restores the Disturbed Interplay Between TNF-α System and HPA Axis - Biological Psychiatry